The Effectiveness of EMS Pelvic Chair Machines: A Scientific and Practical Analysis
February 25, 2026The Benefits of 1927nm Thulium Laser in Medical and Industrial Applications
July 21,2025
Introduction
The 1927nm thulium (Tm) laser has emerged as a groundbreaking technology in both medical and industrial fields due to its unique wavelength characteristics. Unlike traditional laser systems, the 1927nm wavelength offers superior precision, minimal thermal damage, and high absorption in water and soft tissues. This article explores the key advantages of the 1927nm thulium laser, focusing on its medical applications (particularly dermatology and urology) and industrial uses (such as material processing).
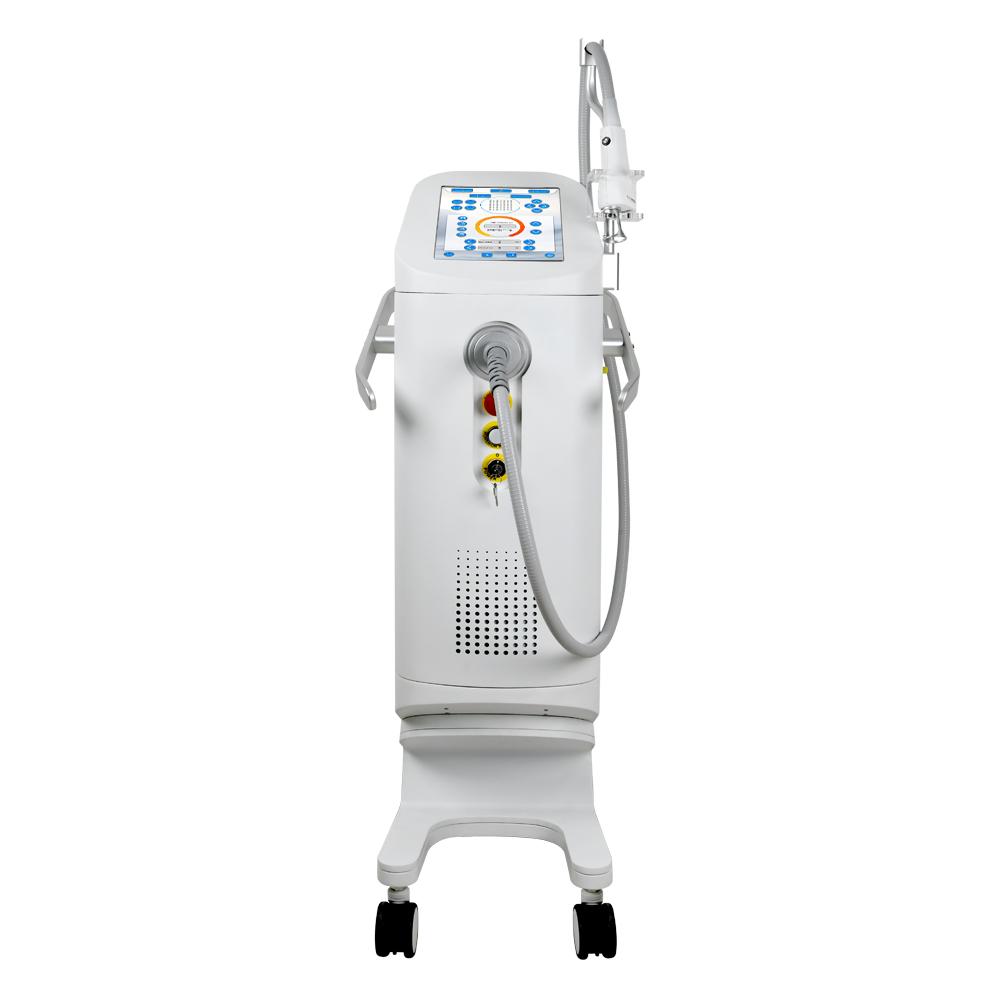
Medical Applications
- Dermatology and Aesthetic Treatments
The 1927nm thulium laser is widely used in dermatology due to its shallow penetration depth (approximately 200–300 microns) and high water absorption. This makes it ideal for:
Skin Resurfacing: Effective in treating fine wrinkles, acne scars, and photoaging by promoting collagen remodeling.
Pigmented Lesion Removal: Targets melanin-rich areas with minimal risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Facial Rejuvenation: Provides fractional ablation while minimizing downtime compared to CO₂ lasers.
- Urology (Kidney Stone and Soft Tissue Ablation)
In urological procedures, the 1927nm thulium laser offers:
Precision Stone Fragmentation: Efficiently breaks down kidney stones with reduced retropulsion compared to Ho:YAG lasers.
Soft Tissue Cutting & Coagulation: Useful in prostate and bladder surgeries due to its hemostatic properties.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
The laser’s ability to cut and coagulate simultaneously reduces bleeding, making it valuable in ENT (ear, nose, throat) and gynecological surgeries.
Industrial and Material Processing Applications
- High-Precision Cutting and Drilling
The 1927nm wavelength is absorbed well by polymers and biological tissues, making it useful for:
Microfabrication: Engraving, drilling, and cutting delicate materials with minimal thermal distortion.
Semiconductor Processing: Used in wafer dicing and thin-film removal.
- Reduced Thermal Damage
Unlike CO₂ lasers (10,600nm), the 1927nm thulium laser generates less heat spread, preserving surrounding materials.
Conclusion
The 1927nm thulium laser stands out for its precision, versatility, and safety in medical and industrial applications. Its ability to combine ablation with coagulation, minimal thermal damage, and high water absorption makes it a superior choice for dermatology, urology, and microfabrication. As technology advances, its applications are expected to expand further, solidifying its role as a leading laser system in multiple industries.