The Effectiveness of EMS Pelvic Chair Machines: A Scientific and Practical Analysis
February 25, 2026The Effectiveness of IPL Machines: A Comprehensive Review
July 14,2025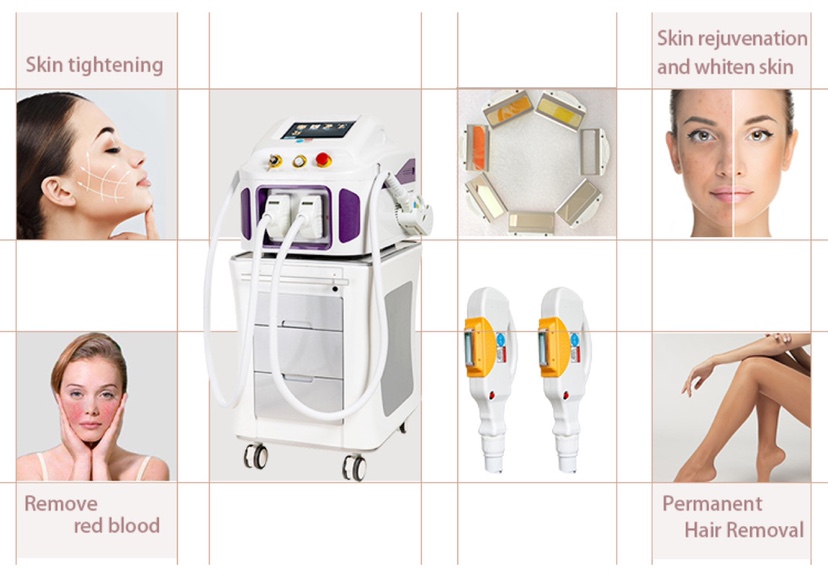
Introduction to IPL Technology
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) is a non-laser, broadband light source used for various dermatological and ophthalmological treatments. Unlike lasers that emit a single wavelength, IPL devices produce a spectrum of light (typically 500–1200 nm) filtered to target specific chromophores in the skin. This versatility has made IPL a popular choice for treating pigmentation disorders, vascular lesions, hair removal, and even ocular conditions like Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD).
Mechanisms of Action
IPL works via selective photothermolysis, where light energy is absorbed by melanin (for pigmentation) or hemoglobin (for vascular lesions), converting into heat to destroy target structures without damaging surrounding tissue. Additionally, IPL stimulates collagen production, improving skin texture and elasticity—a process known as photo-rejuvenation.
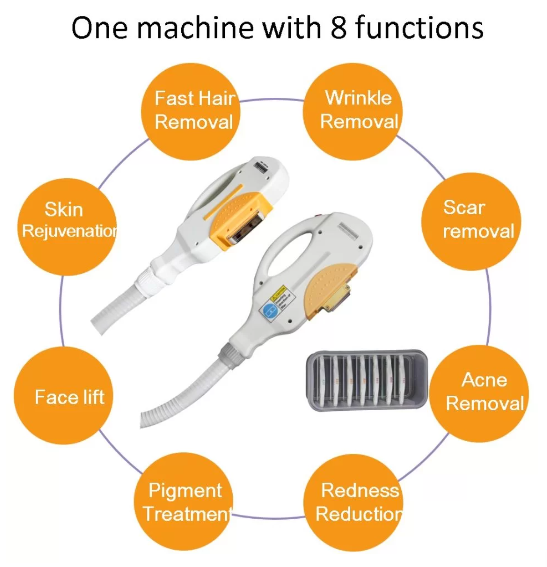
Clinical Applications and Efficacy
1. Skin Rejuvenation & Pigmentation Disorders
- Hyperpigmentation (e.g., sunspots, melasma): Studies show 70–90% clearance of pigmented lesions after 3–5 sessions. Melasma requires maintenance therapy due to high recurrence rates.
- Vascular Lesions (e.g., rosacea, spider veins): IPL reduces erythema and visible vessels by coagulating blood vessels, with success rates exceeding 85% for mild to moderate cases.
- Acne & Scarring: IPL’s anti-inflammatory effects reduce acne lesions by 40–70%, while combined with RF (radiofrequency) improves atrophic scars.
2. Permanent Hair Reduction
IPL is FDA-approved for long-term hair removal, achieving 70–90% reduction after 6–8 sessions. Dark, coarse hair responds best due to higher melanin absorption.
3. Ophthalmology: Treating MGD and Demodex
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: IPL liquefies thickened meibum, improving gland function in 80% of dry eye patients (per 2024 clinical trials).
- Demodex Blepharitis: IPL kills mites via thermal effects, reducing symptoms like itching and redness by 50–60% after 2–3 sessions.
Advantages Over Alternatives
- Non-invasive with minimal downtime (24–48 hours of mild redness).
- Customizable settings (wavelength, pulse duration) for different skin types (Fitzpatrick I–IV).
- Versatility: One device can treat multiple conditions, reducing clinic costs.
Limitations and Risks
- Not suitable for dark skin (Fitzpatrick V–VI) due to higher risk of burns or hypopigmentation.
- Multiple sessions required (3–6 for optimal results).
- Temporary side effects: Swelling, crusting, or paradoxical hair growth in rare cases.

Future Innovations
Emerging technologies like AI-guided IPL automate parameter selection for safer treatments, while nanoparticle-enhanced IPL boosts precision for resistant conditions.
Conclusion
IPL remains a gold-standard for phototherapy due to its efficacy, safety, and multi-condition adaptability. While limitations exist, technological advancements continue to expand its applications, ensuring IPL’s relevance in aesthetic and medical dermatology.